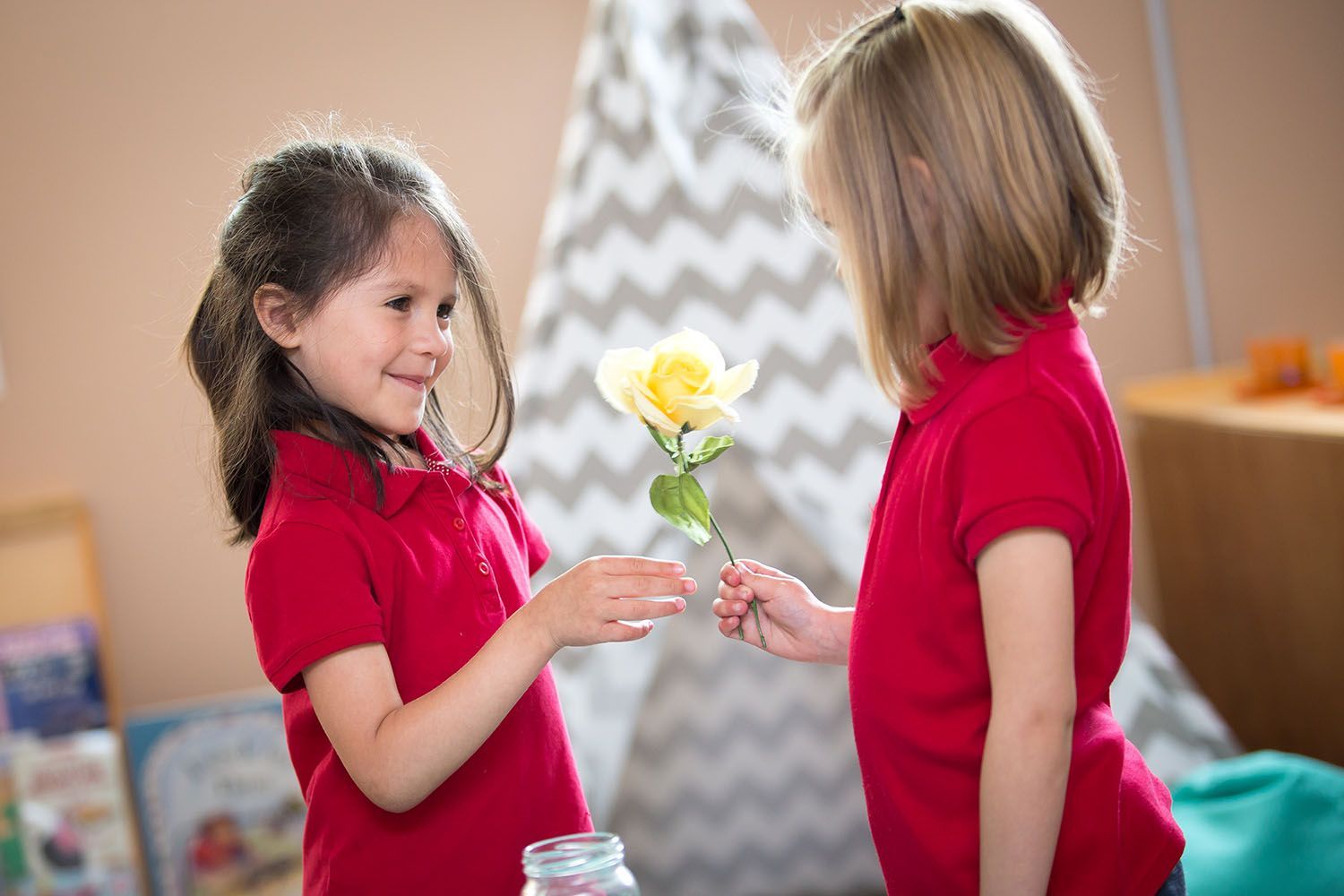
So often when we are bumping up against frustrating behavior from our children, we forget that one very effective way to work through the challenge is to include our children in the process!
Step 1: Identify the Issue
The best way to approach this is to first identify the challenge. Perhaps your child is having a hard time getting ready in the morning. Or maybe you are experiencing bedtime struggles. It might be as seemingly small as cooperation with brushing teeth. Or the issue may revolve around food: packing foods your child will eat, being willing to engage during dinner time, or eating a hearty breakfast before heading to school.
Whatever the problem, first identify it in one simple sentence. Hone in on exactly the challenge or conflict, so it’s easy to state clearly.
Step 2: Ask For Time to Talk
Then you’ll want to find a time when everyone is in a mellow mood, perhaps feeling particularly happy, or even just well-fed and rested. At this point, it’s important to check in with your child by asking something like: “Is now a good time for us to talk?” Or “I’d like to brainstorm with you. Is now a good time?”
It’s best to be at your child’s eye level and/or get together in a comfortable place that encourages connection. Then state the problem as simply and clearly as possible. It is especially important to avoid guilt, blame, shame, and exaggerations. One way to frame the conversation is to start with something like: “I have a situation that I want your help with.”
For example, if your child has been struggling with leaving the house on time in the mornings, you might try stating: “I’ve noticed that our mornings have felt stressful and rushed.”
You can then share the impact or how you feel: “As a result of rushing, I feel anxious and then start to get impatient and a little grumpy.” Followed by what you want: “I’m hoping we can figure out a new routine for our mornings so we can leave the house on time.”
Step 3: Listen to Your Child’s Perspective
After stating your take on things, it’s important to allow your child the space to share how they feel and what they want. All too often, we push our agendas, our perspectives, and our needs onto our children without opening up space and listening to what might be going on for them.
By sharing your perspective without accusation or insistence, and then asking for their feedback and needs, you are demonstrating that you are committed to a collaborative approach. After your child has shared what is happening for them and what they need, you can explore if brainstorming possible solutions could help.
Step 4: Brainstorm Together
If brainstorming seems helpful, get a piece of paper and create a list of ideas or solutions. If your child is younger, you can do the recording. Regardless, free up each other’s thinking by not criticizing or rejecting any ideas during this brainstorming process. Let your imaginations run free. If possible, try to model some “out of the box” thinking and make the process as fun as possible. It’s even okay to get a little silly: “I know! We could invent a robot that puts on your coat and gloves for you!” Offering encouragement can help, too. “That’s a great idea. I never thought of that.” Or “Oh, that gives me another idea!”
It’s important to not go into this process with a hidden agenda. Children are attuned to when we just want things to go our way. In the process of being open to ideas, you’ll likely find some unexpected solutions. Whenever possible, it’s also helpful to generate ideas in which both parties can win.
Step 5: Cross Items off the List
Once you’ve generated a list of possible solutions, go through the list together. Give your child the opportunity to first cross out any ideas that won’t work for them, and you can do the same. In this process, you can both talk about why particular ideas will or won’t work from your particular perspectives. After crossing out ideas, you’ll be left with some options. Together you can pick one of the suggestions, or a combination of ideas, as a solution to try.
Step 6: Test it Out
Emphasize that you can both agree to try the idea and then come back together in about a week to see if it is still working. You can write the agreement on a fresh sheet of paper and, if appropriate, both sign the paper to show a commitment to trying this new idea. Be sure to also thank your child for their cooperation! Be sure to also follow through with checking in with each other after trying out the solution for a week. If it isn’t working, review the list together and see if there is another idea worth trying.
Creating an agreement ahead of time model’s respect. The result? Our children feel more willing to cooperate because the process has been collaborative.
Curious to learn more about how to include children in a problem-solving process? Schedule a time to come in to observe and talk more!