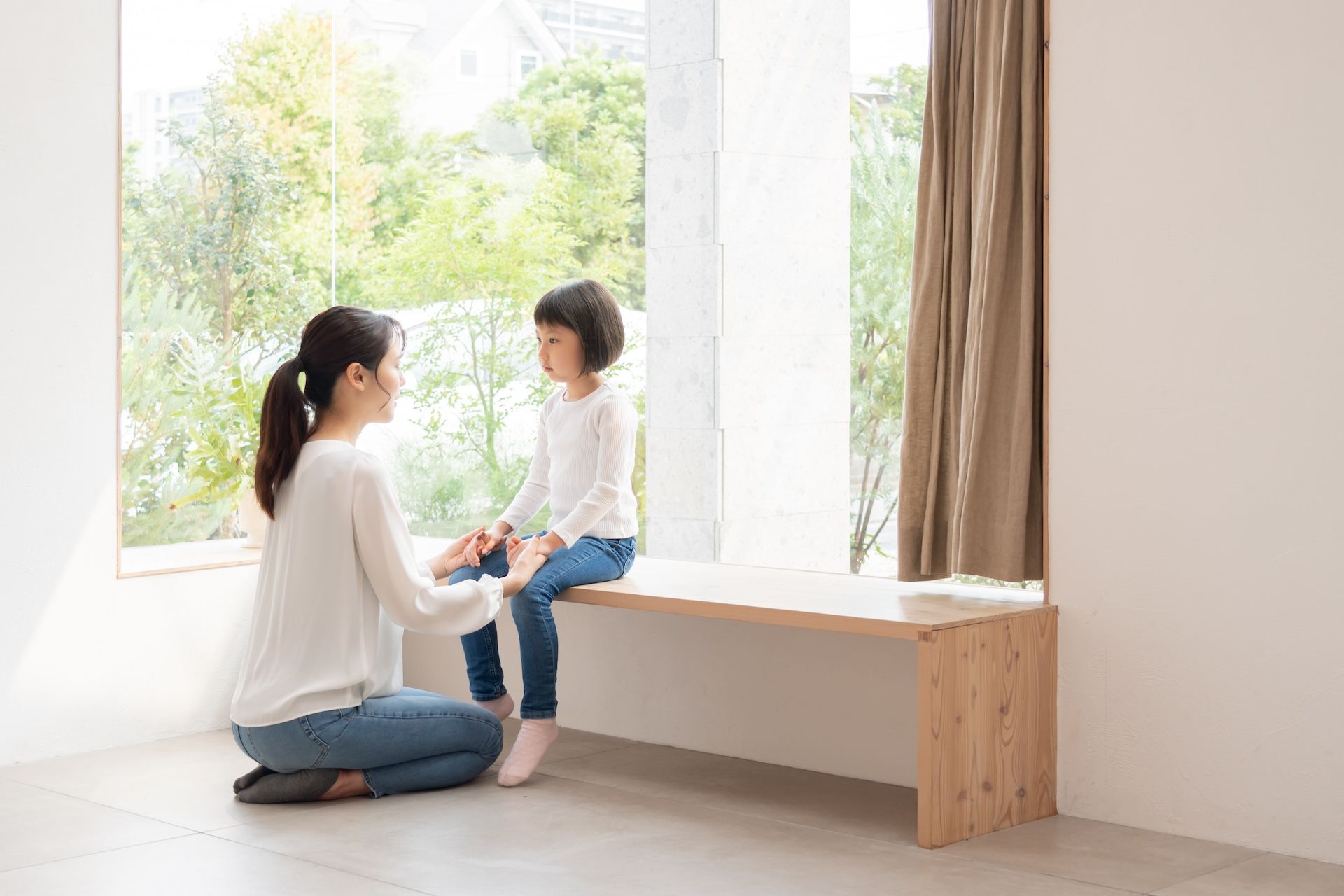
We often get asked the question, “How do you handle discipline issues?” We love this question because in Montessori we think about discipline from a different lens.
We start by being curious because misbehavior is a form of communication. Children want to do well and do the right thing. So what are they trying to tell us when they misbehave?
Unmet Physical Needs
Children often misbehave due to unmet needs. At a very basic, physical level, this might be due to being hungry, tired, or overstimulated. So we look at children’s environment and what could change to better support those needs. Perhaps the problem is due to missing their sleep window and being overtired? Or maybe there’s a need for a more protein-packed breakfast so as to not fall apart mid-morning. It might be that a room full of people is causing too much sensory input and a little time in a quieter space or fresh air is just what’s needed.
Unmet Emotional Needs
Other times children might have unmet emotional needs. Dr. Jane Nelson provides an excellent overview of unmet needs in her Positive Discipline work. Positive Discipline aligns well with Montessori because both are based in teaching children respect, responsibility, and problem-solving skills.
In Positive Discipline, Dr. Nelson outlines unmet emotional needs and categorizes these as four mistaken goals. The essence of Positive Discipline is that children develop behaviors in response to feeling disconnected or powerless in certain situations, so they unconsciously use four strategies to try to get their needs met. Unfortunately, these strategies tend to backfire because the behavior isn’t effective! So our goal is to support children in learning new ways to meet their needs.
Mistaken Goal #1: Attention
The first mistaken goal is attention. We see this when children show behaviors like whining, interrupting, or causing disruptions of some sort. They are seeking attention but can’t yet distinguish between positive attention and negative attention. So when adults respond with annoyance, irritation, or even by giving in, we are inadvertently reinforcing the attention-seeking behavior and children’s underlying belief that they only belong when they have our attention (even if our attention is based on frustration!).
A way to help children meet this need is to offer positive attention, encouragement, and connection at times when they aren’t showing misbehavior. Another proactive approach is to find engaging and meaningful tasks for children to do, which helps provide them with a sense of belonging and connection.
Mistaken Goal #2: Power
When we, as adults, feel angry or challenged in response to children’s behavior, that’s usually a sign that the mistaken goal is one of power-seeking. This kind of behavior can quickly escalate into power struggles, defiance, or even other ways to exert control such as through tantrums or arguing. When children have an unmet goal of power, they have an underlying belief that they can belong only when they are in control or when they can prove that no one can boss them around.
We can support children who have this unmet need by practicing collaborative problem-solving during times when things are already going well. In the moment of challenge, we can avoid power struggles by offering limited choices in a firm but kind way.
Mistaken Goal #3: Revenge
One of the more confusing forms of misbehavior is when children do things that seem intended to hurt others, such as hitting, name-calling, and other destructive actions. When acting this way children are demonstrating that they don’t feel loved so they will hurt others as they feel hurt. What’s tricky is that this behavior often leads to others feeling hurt and wanting to either distance themselves or retaliate.
In order to address this mistaken goal, we need to focus on repairing the relationship and over time addressing the underlying hurt. Empathy and restorative practices help in the process of healing emotional wounds. This mistaken goal requires us to get genuinely curious without any form of accusation or disapproval.
Mistaken Goal #4: Assumed Inadequacy
When children give up easily, withdraw, avoid challenges, or refuse to try, they may be operating under the belief that they belong only by convincing others not to expect anything from them. Our reactions may include feeling helpless, giving up, or even taking over tasks our children were expected to do.
An alternative approach is to encourage small steps toward success and to focus on effort over outcomes. Over time, by breaking up tasks into smaller, manageable parts, and providing side-by-side support without taking over and doing the task for them, we can help children develop more confidence and belief in their abilities.
Shifting our Thinking
So when thinking about misbehavior, we shift our approach to first consider what physical and emotional needs children are trying to communicate. Then we focus on long-term solutions while practicing kindness and firmness. Consistent encouragement, respectful communication, and proactive planning help us address what might typically be seen as “discipline issues” so we can guide children toward healthier behaviors. Part of this includes helping children begin to understand their own needs, learn how to communicate respectfully and establish healthy habits and boundaries.
Do you want to learn more about how school can nurture children’s emotional well-being and their sense of belonging? Schedule a tour to see how we create environments of mutual respect and cooperation!