When visiting a Montessori classroom, it can at first be surprising to see children of a range of ages in one room. Visitors often ask how children of very different sizes and abilities can all be supported and challenged in one classroom. There are many factors, but one reason the mix of ages works so well in Montessori is because we have “three-year cycles.”
What is a Montessori Three-Year Cycle?

In Montessori, children typically enter a classroom as the youngest children and then stay in the same learning community for at least three years. Over the course of those three or so years, they cycle through a rhythm of growth and development.
When children first come into a new classroom it is a bit like what happens when transplanting a perennial flower: they need some time to establish their roots and initially don’t show a great deal of external growth. This first year in a classroom is when children are exploring their environment and making sense of their new community.
During their second year, children are more established and, like perennial flowers, they often show more growth and blossom a bit more. This is when children are experimenting in a learning space where they feel comfortable and established.
By their third year, children are the experts in their community. Similar to perennial flowers, children’s growth becomes exponential and abundant. They truly blossom. The children who have benefited from a three-year cycle show what happens when they have had an opportunity to establish their roots, extend themselves, and then have the time and space to bloom in exciting new ways.
Evolving Roles
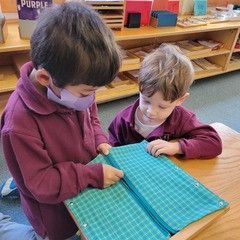
Because children in Montessori classrooms are with each other for a series of years, their learning community becomes a family. As they move through the years together, children get the opportunity to play the role of the youngest, middle, and oldest child, and experience the responsibilities and opportunities that come with those roles.
The younger children look up to their older peers, quickly learning through observation how to behave, what is acceptable, and even what to look forward to in terms of advanced work. The oldest in the class serve as mentors, leaders, and even teachers. As the older students master certain skills or materials, they have the opportunity to share what they have learned and in the process are able to synthesize their learning. Through this mutually beneficial process, children move through the process of developing aspiration, building confidence, and demonstrating mastery.
Consistency of Community

By having a consistent community for at least three years, children are able to build a foundation that serves them in multiple ways. In addition to having time to gain mastery, children establish long-term relationships with their peers and the adults.
With their training and sensitivity to developmental needs, Montessori teachers understand individual children’s learning styles, rhythms, and needs. They can tailor their presentations to the individual, recognizing where and how to help children stretch beyond their comfort zones. As a result, children are able to feel secure enough to take risks in their learning.
One of the additional benefits is that over the course of multiple years, a meaningful and supportive partnership develops between families and the Montessori guides. A consistent community provides support that empowers our children and families.
Zone of Proximal Development

The three-year cycles of Montessori mixed-age classrooms provide children with scaffolding to work in collaboration with a skilled teacher and more knowledgeable peers. Supportive learning environments allow children to make connections that they wouldn’t necessarily be able to make on their own. Psychologist Lev Vygotsky called this scaffolding the “zone of proximal development.” As children grow within their zone of proximal development, they develop more confidence and are able to practice new skills and abilities. They have social support through meaningful, purposeful interactions with others.
As children solidify their learning and consolidate their knowledge, they experience new possibilities for growth in a family-like learning community. This mixed-age experience is an essential component of what we do and our three-year cycles make it possible.
Come see the benefits for yourself! Schedule a tour to get a first-hand glimpse of this three-year cycle in action.