This post is the third installment in our series exploring four stages of human development from a Montessori perspective. The Montessori approach takes a holistic view of growth, recognizing the unique needs of young people at every stage—birth to age six, six to twelve, twelve to eighteen, and eighteen to twenty-four—and adapts learning environments to support natural development at each stage. By understanding these key phases, we can better nurture young individuals as they progress on their journey to maturity.
Adolescence (Age Twelve to Eighteen)
Adolescence is often seen as a turbulent stage in life, sometimes even labeled as dysfunctional or something to endure. However, Dr. Maria Montessori viewed this vital period of human development as a time in our lives that deserves respect and understanding.
In Montessori education, adolescence is honored as a time of transition, a phase of development that, in many ways, mirrors the first six years of life. Just as the early years are marked by rapid transformation and the shaping of the individual, adolescence marks the transformation from childhood into adulthood.
Adolescent Development
The third plane of development, which typically begins at age twelve and continues through the teenage years, is one of significant physical, emotional, and social transformation. This period is characterized by the onset of puberty, hormonal changes, and dramatic physical shifts.
Adolescents, much like children in the first plane of development, experience rapid change, but this time it is in preparation for adulthood and potential child-rearing. As a result, adolescents require more sleep and are more susceptible to health issues (e.g. acne, depression, and eating disorders).
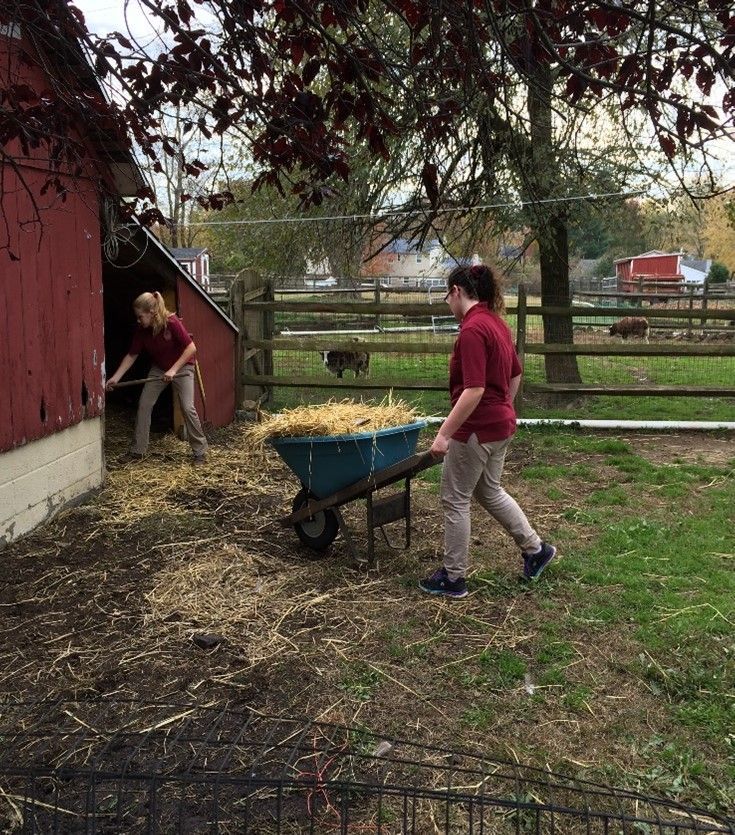
A key focus during this stage is the conquest of social and economic independence. Humans on the journey to adulthood need to function in social organizations, which requires intellectual and social skills. Adolescents also need to experience how economic interdependency works and they want to learn about different roles in economic systems. To do so, they need the awareness and skills to contribute in meaningful ways.
Social engagement is how we function as humans. Economic contribution and interdependency is how we meet our needs. Adolescents are no longer passive observers of society; instead, they strive to become active participants and contributors. Like during the first plane, adolescents learn best through hands-on experiences that benefit society, which reinforces their desire to contribute in meaningful ways.
Adolescents as Social Newborns
Dr. Montessori often referred to early adolescence as the "newborn" stage of adulthood, highlighting the vulnerability and transformation that adolescents undergo. This period of rapid physical and emotional development mirrors the developmental intensity of the first years of life. Adolescents are not just growing in terms of physical stature but also in terms of emotional and social maturity.
Much like a newborn, adolescents are learning how to navigate the complexities of the world around them. They are developing a sense of self and finding their place in society. The challenge of the third plane is to help them build this self-confidence and self-worth, while guiding them through the emotional turbulence that often accompanies this stage.
Holistic Development: Physical, Emotional, and Social Growth
Montessori's approach to adolescence is deeply holistic. We emphasize the importance of addressing the adolescent's physical, emotional, and social needs, recognizing that these areas are interconnected and cannot be separated in the developmental process.
Physical Development
Adolescents undergo significant physical changes during this time, including hormonal fluctuations and rapid growth. Brain development continues with an oversupply of gray matter and pruning of neural pathways, which influences behavior and learning capacity.
Key physical needs include:
- Engaging in physical activity and hands-on work
- Maintaining a healthy diet
- Ensuring adequate sleep
Emotional and Psychological Development
Adolescents experience strong emotional swings and are highly self-conscious. They are forming their identities and are very aware of peer perceptions. Balancing these emotions and navigating their evolving sense of self can be challenging.
Emotional needs include:
- Opportunities to build confidence and independence
- Safe yet challenging environments
- Support in self-expression and identity formation
Social Development
Social connections become increasingly important during adolescence. Adolescents seek peer approval and loyalty and often engage in risk-taking behaviors as they establish their place within their social circles. They learn best through collaboration and social interaction.
Social needs include:
- Opportunities for collaboration with peers
- Mentorship from adults
- Meaningful and relevant social engagement
Moral and Intellectual Development
Dr. Montessori emphasized the adolescent’s sensitivity to issues of justice and personal dignity. This stage is a critical time for developing a strong sense of fairness and the desire to contribute meaningfully to society. As they mature, adolescents begin to understand the value of their contributions to the world around them.
Though their intellectual development might seem secondary due to emotional upheavals, it remains essential. As their brains undergo significant rewiring and neural pruning, adolescents still benefit from intellectual opportunities and challenges, as well as strong moral foundations.
The Role of Work and Contribution
Just as it was in earlier planes of development, work remains a vital aspect of adolescence. Adolescents have a strong desire to contribute to society and have their efforts recognized. Through work and activity, adolescents bolster their self-esteem and gain a sense of accomplishment.
The educational model proposed by Dr. Montessori focuses on land-based work and cooperative community living, which provide ways for adolescents to engage in meaningful activities. This model supports adolescents’ physical well-being, fosters social development, and prepares them for economic independence. Through hands-on work, adolescents not only contribute to their immediate communities but also develop a sense of responsibility and understanding of the value of work.
Supporting Adolescents Through Their Development
To meet the developmental needs of adolescents, we need to offer supportive environments. Dr. Montessori envisioned a community where adolescents could live and work together, gaining both physical and emotional nourishment. Providing opportunities for physical activity, collaboration, and self-expression helps adolescents develop into confident, capable adults.
Adolescents need both freedom and guidance. While they push away from adults as they seek independence, they still require boundaries, structure, and mentorship. Adults play a critical role in supporting adolescents as they navigate this transformative stage.
Understanding adolescence through the Montessori lens allows us to appreciate this period as one of profound transformation. By honoring the physical, emotional, social, and moral development of adolescents, we can provide them with the support they need to transition confidently into adulthood. With a holistic approach that integrates meaningful work, opportunities for self-expression, and guidance from adults, adolescents can be empowered to become the capable, interdependent adults society needs. Visit our school today to learn more!