Young children are constantly absorbing information about the world around them! Some of it is very concrete, while some is abstract.
Color as an Abstraction
Think about the color red. Red as a quality does not exist in nature. Red can be represented in physical things, but you can’t bring “red” to another person. We can find a red apple, a red street sign, a red flower, but we can’t find just red. Red is an abstraction.
In Montessori environments, we are mindful of how we introduce young children to these kinds of abstractions. We try to represent the intangible quality in a physical form and to isolate it so that children can really focus on the quality and the language connected to that attribute. Every variable is held constant except for the one characteristic to experience and explore. We do this to give children the clearest, most precise images we can.
These materials that we use to introduce the abstract concept of color are called the color tablets because each color is represented on a tablet. The tablet with red looks exactly like every other tablet in our color box, except for its color. Each tablet has the same size, weight, and shape. The only variation is the color. This materialized abstraction allows us to put “red” in the child’s hands to experience and explore. The Montessori color tablets are organized into three boxes.
First Color Tablet Box

The first color tablet box is composed of three pairs of color tablets: red, blue, and yellow. These primary colors represent the extremes of color. With this first box we awaken children’s sensory awareness by introducing how to pair the matching color tablets. There are two of each variable and children find the mates. Cognitively it is easier for children to notice sameness than difference.
In this first stage, we also demonstrate how to handle the material and how to experience the sense. If a child can’t distinguish the extremes of the set, we get important information about their sensorial perception. Sometimes the child isn’t successful at this first stage because they aren’t yet comprehending the concept of sameness. Thus we must be very careful to let children know how we are pairing the items by finding the matching the tablet that looks exactly like the one we have selected first. This isn’t just random pairing, but rather is based upon a specific perception. Often children don’t spend too long with this first box of color tablets, although some young children will be drawn to the simple beauty of the three primary colors.
Second Color Tablet Box
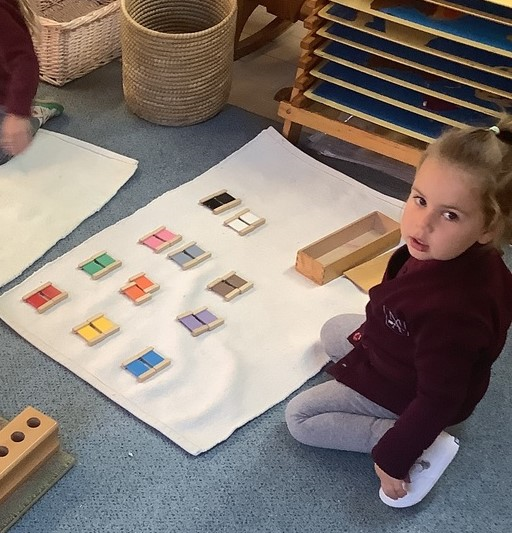

With color box two, the focus is still on finding similarities, however, there are more variables. For example, color box two has primary colors and secondary colors, as well as brown, grey, black, and white. This adds more variables for children to search through to find the match and thus requires them to use a finer level of discrimination. When we add more variables, the differences between them become smaller and not as extreme. This challenges children’s exactness and precision.
Third Color Tablet Box
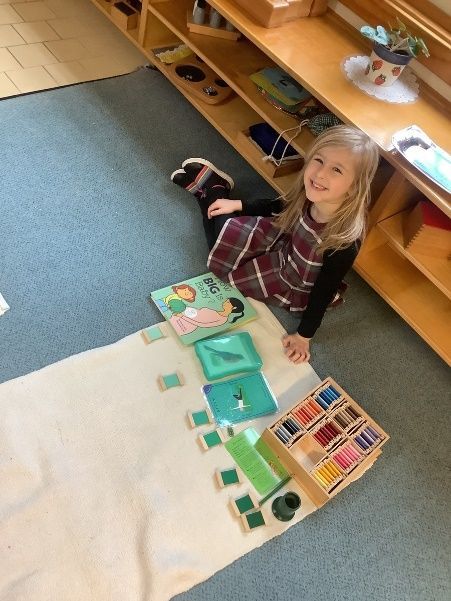

The third box of color tablets is divided into seven or eight compartments each with a gradation of one color from dark to light. Children begin using this box when they have been successful pairing with more variables because grading by shade requires a higher level of discriminating difference. Children’s attention has to be focused on a slight unit of difference. Is the blue just lighter than the last shade of blue? This is cognitively much harder!
Just these three steps are not enough to ensure the maximum amount of depth of experience with the materials. Thus, we extend work with the color boxes by offering language and memory games.
Language Extensions
After children have some experience with the material and we observe that they are successful in consistently pairing two colors together, we offer children language to accompany the abstraction. Language fixes the sensorial quality in their minds and aids memory and recall. We don’t want to give language to images that are not clear, because that confuses children. When children are successful pairing colors, we offer the names of the colors. Then when children are successful in grading the shades of a color, we offer the comparative terms (darker than, lighter than) and superlative expressions (darkest red, lightest red).
Memory Games
Memory games help children discover sensorial qualities in the world around them. In the first memory game, children put one set of the paired color tablets in one location and the second set in random order somewhere else in the room. The trick is to have the second location be just far enough away so as to allow enough time for children to retain a memory of the color. To play the game, children place a “memory marker” next to one of the color tablets lined up in the first location. They then hold that color, such as “red”, in mind and walk to the second location. There they find the red tablet and bring it back to place it by its mate. Children then move the memory marker to another color tablet and continue.
When children are successful with this, they can try a harder variation of this game in which they use a tray to place the second set of color tablets in scattered locations around the room. When children go to find the matching color tablet, they must retain the impression in their memory for a longer time and not be distracted by the other things they see as they walk around the room.
Children can also play a game of matching each color tablet to a material in the classroom. For this game, children use the memory marker to indicate which color tablet they are using. They then study the color tablet, leave it on the rug or table, and then search the environment for an object that has the same exact shade of the color. When they find the object, they bring it back and place it next to the selected color tablet.
Keys to the World
If we think about the world of color, we realize there are an infinite number of colors, shades, etc. We don’t give children every color of the world. We give the keys: the primary colors, then the secondary colors, then black and white, and a few other colors. Every other color is made from those keys!
The color tablets are one of the more lovely and inviting materials we use in the Children’s House or primary classrooms. Come visit our school and see how young children internalize these kinds of abstract concepts and, in the process, develop a refined sensorial ability!